 What Is Breast Cancer?
What Is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer is a disease in which cells in the breast grow out of control. There are different kinds of breast cancer. The kind of breast cancer depends on which cells in the breast turn into cancer.
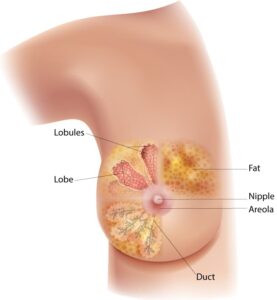
Breast cancer can begin in different parts of the breast. A breast is made up of three main parts: lobules, ducts, and connective tissue. The lobules are the glands that produce milk. The ducts are tubes that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which consists of fibrous and fatty tissue) surrounds and holds everything together. Most breast cancers begin in the ducts or lobules.
Breast cancer can spread outside the breast through blood vessels and lymph vessels. When breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it is said to have metastasized.
Kinds of Breast Cancer
The most common kinds of breast cancer are—
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. The cancer cells begin in the ducts and then grow outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma. Cancer cells begin in the lobules and then spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by. These invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
There are several other less common kinds of breast cancer, such as Paget’s disease, medullary, mucinous, and inflammatory breast cancer.
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a breast disease that may lead to invasive breast cancer. The cancer cells are only in the lining of the ducts, and have not spread to other tissues in the breast.
What Are the Symptoms of Breast Cancer?
Different people have different symptoms of breast cancer. Some people do not have any signs or symptoms at all.

Some warning signs of breast cancer are—
- New lump in the breast or underarm (armpit).
- Thickening or swelling of part of the breast.
- Irritation or dimpling of breast skin.
- Redness or flaky skin in the nipple area or the breast.
- Pulling in of the nipple or pain in the nipple area.
- Nipple discharge other than breast milk, including blood.
- Any change in the size or the shape of the breast.
- Pain in any area of the breast.
Keep in mind that these symptoms can happen with other conditions that are not cancer.
If you have any signs or symptoms that worry you, be sure to see your doctor right away.
What Is a Normal Breast?
No breast is typical. What is normal for you may not be normal for another woman. Most women say their breasts feel lumpy or uneven. The way your breasts look and feel can be affected by getting your period, having children, losing or gaining weight, and taking certain medications. Breasts also tend to change as you age. For more information, see the National Cancer Institute’s Breast Changes and Conditions.
What Do Lumps in My Breast Mean?
Many conditions can cause lumps in the breast, including cancer. But most breast lumps are caused by other medical conditions. The two most common causes of breast lumps are fibrocystic breast condition and cysts. Fibrocystic condition causes noncancerous changes in the breast that can make them lumpy, tender, and sore. Cysts are small fluid-filled sacs that can develop in the breast.
What Are the Risk Factors for Breast Cancer?
Studies have shown that your risk for breast cancer is due to a combination of factors. The main factors that influence your risk include being a woman and getting older. Most breast cancers are found in women who are 50 years old or older.
Some women will get breast cancer even without any other risk factors that they know of. Having a risk factor does not mean you will get the disease, and not all risk factors have the same effect. Most women have some risk factors, but most women do not get breast cancer. If you have breast cancer risk factors, talk with your doctor about ways you can lower your risk and about screening for breast cancer.
Risk Factors You Cannot Change
- Getting older. The risk for breast cancer increases with age. Most breast cancers are diagnosed after age 50.
- Genetic mutations. Women who have inherited changes (mutations) to certain genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, are at higher risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
- Reproductive history. Starting menstrual periods before age 12 and starting menopause after age 55 expose women to hormones longer, raising their risk of getting breast cancer.
- Having dense breasts. Dense breasts have more connective tissue than fatty tissue, which can sometimes make it hard to see tumors on a mammogram. Women with dense breasts are more likely to get breast cancer.
- Personal history of breast cancer or certain non-cancerous breast diseases. Women who have had breast cancer are more likely to get breast cancer a second time. Some non-cancerous breast diseases such as atypical hyperplasia or lobular carcinoma in situ are associated with a higher risk of getting breast cancer.
- Family history of breast or ovarian cancer. A woman’s risk for breast cancer is higher if she has a mother, sister, or daughter (first-degree relative) or multiple family members on either her mother’s or father’s side of the family who have had breast or ovarian cancer. Having a first-degree male relative with breast cancer also raises a woman’s risk.
- Previous treatment using radiation therapy. Women who had radiation therapy to the chest or breasts (for instance, treatment of Hodgkin’s lymphoma) before age 30 have a higher risk of getting breast cancer later in life.
- Exposure to the drug diethylstilbestrol (DES). DES was given to some pregnant women in the United States between 1940 and 1971 to prevent miscarriage. Women who took DES, or whose mothers took DES while pregnant with them, have a higher risk of getting breast cancer.
Risk Factors You Can Change

Being physically active can help lower your risk of getting breast cancer.
- Not being physically active. Women who are not physically active have a higher risk of getting breast cancer.
- Being overweight or having obesity after menopause. Older women who are overweight or have obesity have a higher risk of getting breast cancer than those at a healthy weight.
- Taking hormones. Some forms of hormone replacement therapy (those that include both estrogen and progesterone) taken during menopause can raise risk for breast cancer when taken for more than five years. Certain oral contraceptives (birth control pills) also have been found to raise breast cancer risk.
- Reproductive history. Having the first pregnancy after age 30, not breastfeeding, and never having a full-term pregnancy can raise breast cancer risk.
- Drinking alcohol. Studies show that a woman’s risk for breast cancer increases with the more alcohol she drinks.
Research suggests that other factors such as smoking, being exposed to chemicals that can cause cancer, and changes in other hormones due to night shift working also may increase breast cancer risk.
Who Is at High Risk for Breast Cancer?
If you have a strong family history of breast cancer or inherited changes in your BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, you may have a high risk of getting breast cancer. You may also have a high risk for ovarian cancer.
Talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk, such as medicines that block or decrease estrogen in your body, or surgery.
What Can I Do to Reduce My Risk of Breast Cancer?
Many factors over the course of a lifetime can influence your breast cancer risk. You can’t change some factors, such as getting older or your family history, but you can help lower your risk of breast cancer by taking care of your health in the following ways—- Keep a healthy weight.
- Be physically active.
- Choose not to drink alcohol, or drink alcohol in moderation.
- If you are taking, or have been told to take, hormone replacement therapy or oral contraceptives (birth control pills), ask your doctor about the risks and find out if it is right for you.
- Breastfeed your children, if possible.
- If you have a family history of breast cancer or inherited changes in your BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, talk to your doctor about other ways to lower your risk.
